Telematics tracking system is rapidly changing the way businesses manage their operations and resources, transforming data into actionable insights. From real-time vehicle monitoring to advanced analytics, this technology integrates GPS and onboard diagnostics to enhance efficiency and drive cost savings. As industries evolve, understanding telematics becomes essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
The components of telematics tracking systems have evolved significantly, making them indispensable tools for fleet management, logistics, and personal vehicle tracking. With a variety of systems available today, organizations can choose solutions tailored to their specific needs, ensuring they leverage the full potential of this innovative technology.
Introduction to Telematics Tracking System
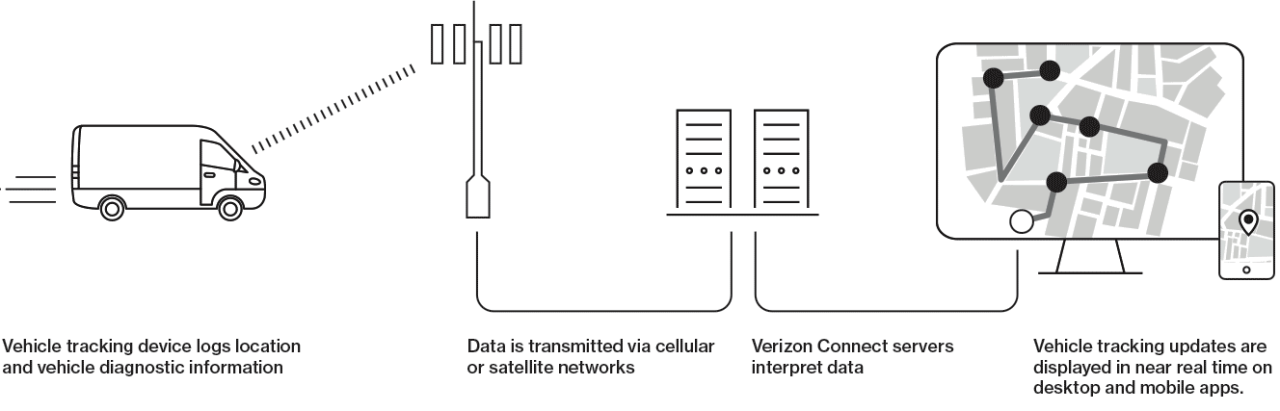
Telematics tracking systems combine telecommunications and monitoring to provide real-time data about vehicles, assets, or individuals. These systems leverage GPS technology and onboard diagnostics to capture and transmit information about location, speed, fuel consumption, and much more. The integration of various technologies allows for enhanced efficiency, safety, and operational management in numerous industries, making telematics a vital resource in today’s fast-paced world.The components of a telematics tracking system typically include a GPS receiver, onboard diagnostic equipment, a telematics control unit, and communication networks that enable data transfer.
The GPS receiver determines the geographical location of the asset being monitored, while the onboard diagnostic equipment collects performance data from the vehicle. The telematics control unit processes this information and communicates it through cellular, satellite, or internet networks to a central server, where it can be accessed by users for analysis and reporting.
Evolution of Telematics Technology
Over the years, telematics technology has undergone significant advancements, transforming from basic vehicle tracking systems to comprehensive solutions that encompass various functionalities. Initially, telematics focused on vehicle location tracking, primarily using simple GPS systems. However, the advent of the internet and mobile technologies has propelled telematics into a new era, offering a plethora of services that enhance fleet management, driver safety, and vehicle maintenance.Key milestones in the evolution of telematics technology include:
- Early 2000s: Introduction of GPS tracking devices in fleet management, providing basic location tracking.
- Mid-2000s: Integration of cellular technology enabled real-time data transmission, leading to improved operational insight.
- Late 2000s: Development of advanced analytics and reporting tools, allowing for better decision-making and resource allocation.
- 2010s: Expansion of telematics to include driver behavior monitoring and vehicle health diagnostics, enhancing safety and reducing costs.
- Present: Advanced telematics systems now incorporate artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), providing predictive analytics, automated reporting, and even remote vehicle control capabilities.
As telematics technology continues to evolve, its applications span beyond transportation, influencing industries such as logistics, insurance, and public safety, thereby shaping the future of how we manage and track assets.
Types of Telematics Tracking Systems
Telematics tracking systems have revolutionized the way businesses monitor and manage their assets. Various types of telematics systems cater to different operational needs and industry requirements, providing users with real-time data about their vehicles and equipment. Understanding these types allows businesses to choose the most suitable tracking solution for their specific applications.Telematics tracking systems can be broadly classified into two categories: active tracking systems and passive tracking systems.
Each type has unique features that cater to different operational requirements, and understanding their differences is crucial for effective fleet management.
Active and Passive Tracking Systems
Active tracking systems continuously transmit data in real-time, allowing users to monitor their assets’ location and status instantaneously. This type of system is particularly useful for businesses that require immediate visibility and timely responses, such as logistics and emergency services. Locations and speeds of the vehicles are updated regularly, ensuring accurate tracking information.In contrast, passive tracking systems collect and store data for later retrieval.
These systems do not provide real-time updates; instead, they allow users to download the data at scheduled intervals or when necessary. They are often used in industries where real-time tracking is not critical, such as construction and car rental services. The following list highlights the key differences between active and passive tracking systems:
- Data Transmission: Active systems transmit data in real-time, while passive systems store data for future access.
- Cost: Active systems tend to be more expensive due to the ongoing data transmission fees, whereas passive systems usually have lower initial costs.
- Use Cases: Active systems are ideal for fleet management and emergency response, while passive systems suit industries like construction and rental services.
- Data Accessibility: Active systems offer immediate access to location and performance metrics, and passive systems require manual data retrieval.
Industries Utilizing Telematics Systems
Telematics systems find applications across various sectors, each leveraging the technology to enhance efficiency and safety. Here are some examples of industries that utilize these systems effectively:
- Logistics and Transportation: Companies in this sector utilize telematics for real-time vehicle tracking, route optimization, and monitoring driver behavior.
- Construction: Construction companies benefit from telematics by tracking equipment usage, maintenance schedules, and asset location.
- Insurance: Insurers use telematics data to assess driving behaviors, potentially offering lower premiums for safer driving practices.
- Agriculture: Farmers employ telematics to monitor machinery performance, optimize resource usage, and improve crop yield through precision farming techniques.
Each industry harnesses telematics tracking systems to address specific challenges, streamline operations, and gain a competitive edge. The adaptability of these systems makes them invaluable for optimizing workflows and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Importance of Telematics Tracking Systems
The implementation of telematics tracking systems is becoming increasingly vital for modern businesses, particularly those with fleets or mobile assets. These systems provide real-time data on vehicle location, driver behavior, and operational efficiency. By leveraging this information, companies can enhance their productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall service delivery.Telematics tracking systems offer numerous benefits that can transform business operations. These systems enable organizations to monitor and manage their resources more effectively, leading to significant improvements in performance and cost management.
Here’s a closer look at the importance of telematics tracking systems in business.
Benefits of Implementing a Telematics Tracking System
One of the primary advantages of adopting a telematics tracking system is the ability to gather comprehensive data on fleet operations. This data can be utilized to make informed decisions that can enhance business outcomes.
- Improved Fleet Management: Businesses can track vehicle locations in real-time, ensuring better routing and timely deliveries.
- Enhanced Accountability: Monitoring driver behavior helps enforce safety protocols and encourages responsible driving.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to detailed reports aids in strategic planning and operational adjustments.
Potential Cost Savings Associated with Telematics Tracking
Telematics tracking systems can lead to substantial cost savings, making them an attractive investment for businesses. By providing insights into various operational aspects, companies can identify unnecessary expenditures and optimize their resources.
- Fuel Efficiency: Real-time tracking minimizes idling time and optimizes routes, resulting in lower fuel consumption.
- Maintenance Costs: Predictive maintenance alerts can prevent costly repairs and extend vehicle lifespans.
- Insurance Premiums: Improved safety records can lead to lower insurance costs as risks decrease.
Operational Efficiency Improvements
The deployment of telematics tracking systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency across various business functions. By utilizing the data collected, businesses can streamline their workflows and increase productivity.
- Resource Allocation: Businesses can allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that vehicles and personnel are used to their fullest potential.
- Reduced Downtime: Quick identification of issues and prompt responses can minimize downtime and keep operations running smoothly.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improved delivery times and service reliability can lead to higher customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Key Features of Telematics Tracking Systems

Modern telematics tracking systems are equipped with a variety of essential features that enhance vehicle monitoring and management. These features provide businesses and individuals with the necessary tools to increase efficiency, enhance safety, and optimize fleet operations. Understanding these features is vital in selecting the right system to meet specific requirements.One of the most critical aspects of telematics tracking systems is their ability to offer both real-time tracking and historical data tracking capabilities.
Each serves a distinct purpose and brings unique advantages to users.
Real-Time Tracking vs. Historical Data Tracking
Real-time tracking allows users to monitor the exact location of vehicles as they move, making it a crucial feature for fleet management. This capability enables businesses to ensure timely deliveries, improve route optimization, and enhance driver accountability. By receiving instant updates, companies can react swiftly to unforeseen circumstances such as traffic delays or vehicle breakdowns. In contrast, historical data tracking provides insights into past journeys and vehicle performance over time.
This feature is essential for analyzing trends, monitoring driver behavior, and assessing fuel efficiency over a specific period. Historical data can also be invaluable for compliance and reporting purposes, allowing businesses to maintain accurate records of vehicle usage.The combination of real-time and historical tracking allows users to develop comprehensive insights into their operations, leading to more informed decision-making.
Significance of Geofencing in Telematics Systems
Geofencing is a groundbreaking feature that enhances telematics systems’ functionality. It involves creating virtual boundaries around specific geographical areas, enabling users to receive alerts when a vehicle enters or exits these zones. This capability plays a significant role in improving security, ensuring compliance, and enhancing operational efficiency.Utilizing geofencing can lead to several key advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Geofencing provides real-time alerts for unauthorized vehicle movements, allowing swift action to prevent theft or misuse.
- Improved Compliance: Businesses can ensure that drivers adhere to designated routes or areas, which is particularly important in sectors such as waste management or delivery services.
- Operational Efficiency: By setting geofences for delivery locations, businesses can optimize logistics and reduce travel time, ultimately saving fuel costs.
By leveraging geofencing technology, organizations can significantly enhance their operational control and mitigate potential risks associated with fleet management.
“The integration of geofencing in telematics systems represents a leap forward in the ability to manage and secure vehicle fleets effectively.”
Applications of Telematics Tracking Systems
Telematics tracking systems have become an integral part of various industries, specifically in fleet management, logistics, transportation, and personal vehicle tracking. The ability to gather and analyze data in real-time enhances operational efficiency, safety, and customer satisfaction. This segment will explore the diverse applications of telematics systems and how they positively impact different sectors.
Telematics in Fleet Management
In fleet management, telematics systems provide comprehensive data regarding vehicle location, speed, and driver behavior, which are crucial for optimizing operations. By implementing telematics, fleet managers can reduce fuel consumption, improve maintenance schedules, and enhance driver safety. The following are key applications of telematics in fleet management:
- Real-Time Vehicle Monitoring: Fleet managers can track vehicle movements in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments based on traffic conditions or delivery changes.
- Route Optimization: Telematics can analyze traffic patterns and suggest the most efficient routes, minimizing delays and reducing operational costs.
- Driver Performance Management: Systems can assess driving habits, providing insights that lead to safer driving practices and lower accident rates.
- Maintenance Alerts: Predictive maintenance functions alert managers when a vehicle needs servicing, preventing breakdowns and extending vehicle life.
Telematics in Logistics and Transportation
The logistics and transportation industries leverage telematics systems to enhance supply chain management and improve customer service. With accurate tracking and reporting, companies can maintain high levels of operational efficiency. Notable applications include:
- Asset Tracking: Telematics technology enables real-time tracking of shipments, ensuring visibility throughout the logistics process and enhancing accountability.
- Inventory Management: By integrating telematics with inventory systems, companies can better manage stock levels and reduce waste, leading to cost savings.
- Delivery Time Prediction: Advanced algorithms predict delivery times based on current traffic and weather data, allowing companies to provide accurate estimates to customers.
- Emergency Response: In case of vehicle breakdowns or accidents, telematics can signal emergency services automatically, reducing response times and improving safety outcomes.
Telematics in Personal Vehicle Tracking
Telematics systems are not limited to commercial use; they have also found applications in personal vehicle tracking. Individuals use telematics for various reasons, including safety and convenience. Here are some common applications:
- Stolen Vehicle Recovery: Many telematics systems enable users to track their vehicle’s location, making it easier to recover stolen vehicles.
- Driver Behavior Monitoring: Parents can monitor the driving habits of young drivers, promoting safer driving practices and reducing risk.
- Maintenance Reminders: Personal telematics can track vehicle health and notify owners when maintenance is due, helping to avoid costly repairs.
- Travel History Records: Users can review their travel history, providing insights for personal budget tracking or route planning for future trips.
Challenges and Limitations
Implementing telematics tracking systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency and data analysis. However, it’s essential to recognize the challenges and limitations that accompany these advanced technologies. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for businesses looking to adopt telematics solutions effectively.
Common Challenges in Implementation
While telematics systems offer numerous advantages, organizations often encounter several challenges when integrating these technologies. Some of the key issues include:
- High Initial Costs: The investment required for hardware, software, and installation can be substantial, especially for small to mid-sized companies.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Merging telematics solutions with current IT infrastructure can lead to compatibility issues, requiring additional resources and time.
- User Training: Employees need adequate training to utilize telematics systems effectively, which may necessitate ongoing support and development.
- Data Overload: The vast amount of data generated can overwhelm users, making it difficult to derive actionable insights without proper analytics tools.
Data Privacy Concerns
With the increasing reliance on telematics technology, data privacy has emerged as a significant concern. Organizations must navigate the complexities of safeguarding sensitive information, particularly when dealing with GPS tracking and personal data.
The protection of individual privacy rights must be balanced with the operational benefits gained from data collection.
Several aspects contribute to these privacy concerns:
- Tracking Personal Activities: Continuous monitoring can lead to breaches of personal privacy, raising ethical questions about surveillance.
- Data Breaches: Storing large volumes of sensitive data increases the risk of cyberattacks, potentially exposing confidential information.
- Compliance with Regulations: Organizations must adhere to data protection regulations such as GDPR, which can complicate data management and usage.
Limitations in Specific Industries
Telematics systems are not universally applicable across all sectors, and certain industries face unique limitations when implementing these technologies. For instance:
- Healthcare: Concerns regarding patient confidentiality can restrict the use of telematics for tracking medical equipment or personnel.
- Construction: The dynamic nature of construction sites can lead to inconsistent GPS signals, resulting in unreliable tracking data.
- Agriculture: Variability in rural areas can hinder connectivity, making it difficult for farmers to leverage real-time tracking effectively.
In each of these industries, overcoming these limitations requires tailored solutions and careful consideration of the specific operational context.
Future Trends in Telematics: Telematics Tracking System
The telematics industry is on the cusp of transformation, driven by rapid advancements in technology. As telematics tracking systems evolve, several emerging trends are expected to shape their functionality and user experience. Key areas of growth include the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the capabilities of these systems.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Telematics
A variety of emerging technologies are set to redefine telematics tracking systems. These advancements not only streamline operations but also improve efficiency and safety measures in various fields.
5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks is expected to significantly enhance communication speeds between devices, allowing for real-time data transmission. This leap in connectivity can greatly improve fleet management and tracking accuracy.
Blockchain Technology
Implementing blockchain can enhance data security and integrity, ensuring that the information collected by telematics systems remains tamper-proof. This can be particularly beneficial in industries that require high accountability, such as logistics and insurance.
Advanced Sensors
The development of more sophisticated sensors can provide richer data from vehicles, including conditions such as tire pressure, engine performance, and fuel efficiency, leading to more informed decision-making.
Integration of IoT with Telematics Systems
The convergence of IoT with telematics opens a new frontier in data collection and analysis. IoT devices can communicate with telematics systems to gather and transmit a wide array of data points, transforming the way information is processed and utilized.The synergy between IoT and telematics allows for:
Enhanced Data Collection
IoT devices can collect data from various sources including vehicles, infrastructure, and other devices, providing a holistic view of operations.
Predictive Maintenance
Real-time data gathered through IoT devices enable predictive analytics, allowing companies to anticipate and address maintenance issues before they escalate, thereby reducing downtime.
Smart Traffic Management
Integrating IoT with telematics can facilitate intelligent transportation systems, which optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion through real-time data analysis.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Telematics
Artificial intelligence is becoming a cornerstone of modern telematics systems, enabling enhanced functionality and smarter decision-making processes. The use of AI algorithms can significantly augment the capabilities of telematics applications.Key contributions of AI in telematics include:
Data Analysis and Insights
AI can analyze vast amounts of data collected through telematics, identifying trends and patterns that are not easily discernible by human analysts. This leads to actionable insights that can optimize operations.
Driver Behavior Monitoring
AI systems can evaluate driver behavior in real-time, providing feedback and coaching to enhance safety and reduce risk. This can lead to lower insurance premiums and improved safety records.
Automated Reporting
AI can simplify the reporting process by automating data aggregation and analysis, allowing for timely and accurate reporting without manual input.
The integration of emerging technologies, IoT, and AI is set to revolutionize the telematics landscape, increasing safety, efficiency, and operational effectiveness across various industries.
Selecting the Right Telematics Tracking System
Choosing the right telematics tracking system is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their operational efficiency and gain insights into their fleet management. With numerous options available in the market, careful evaluation of different solutions is essential to ensure that a business selects a provider that aligns with its specific needs and goals. This guide will walk you through the key criteria to consider when evaluating telematics tracking systems.
Criteria for Evaluating Telematics Providers
When selecting a telematics tracking system, businesses should consider several key factors that impact functionality, usability, and overall effectiveness. Understanding these criteria can help in making a well-informed decision.
- Scalability: The system should accommodate growth. As your fleet size increases, the telematics solution must seamlessly adapt without significant additional investment.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure compatibility with existing systems (like ERP or CRM) to facilitate data sharing and operational efficiency.
- User Interface: A user-friendly interface is essential for quick adoption by staff. The system should be intuitive, requiring minimal training to operate.
- Data Accuracy: Look for systems that provide real-time and precise data tracking. Accurate data ensures better decision-making.
- Security Features: Since telematics systems handle sensitive information, robust security measures must be in place to protect against data breaches.
- Customer Support: Consider the level of support offered. Reliable customer service can greatly reduce downtime and troubleshooting challenges.
- Pricing Structure: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the solution. This involves understanding not just the initial setup costs but ongoing fees and potential hidden charges.
Comparison of Leading Telematics Solutions
Creating a comparison chart of leading telematics tracking systems can facilitate a clearer understanding of how different providers stack up against each other. Below is an illustrative example of criteria that can be included in such a comparison:
| Provider | Scalability | Integration | User Interface | Data Accuracy | Security | Support | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | High | Excellent | Intuitive | Real-Time | Advanced | 24/7 | $$$ |
| Provider B | Medium | Good | User-Friendly | High | Standard | Business Hours | $$ |
| Provider C | Low | Limited | Complex | Moderate | Basic | Limited | $ |
“Selecting the right telematics system can significantly enhance operational efficiency and data-driven decision-making.”
Case Studies of Successful Implementation
In the realm of telematics tracking systems, numerous companies have successfully integrated these technologies into their operations, achieving remarkable outcomes. By examining real-world case studies, we can identify the specific benefits and improvements that telematics has brought to various industries. These examples demonstrate how effective implementation can lead to enhanced productivity, cost savings, and improved safety measures.
Logistics and Fleet Management
One notable example comes from a leading logistics company that adopted a telematics system to monitor its fleet of delivery trucks. By utilizing GPS tracking, the company gained real-time visibility into vehicle locations, enabling better route optimization. This resulted in a significant reduction in fuel consumption, estimated at 15%, and improved delivery times by 20%. The system also provided insights into driver behavior, leading to a decrease in accidents and a 25% reduction in insurance costs.
The success of this implementation can be attributed to several key factors:
- Data-Driven Decisions: The ability to analyze vehicle performance and driver behavior helped the company make informed decisions.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamless integration with the company’s logistics software ensured smooth operations and enhanced data accuracy.
- Training and Support: Comprehensive training for drivers and management on utilizing the system effectively played a crucial role in maximizing its potential.
Public Transportation Enhancement, Telematics tracking system
Another successful case is from a metropolitan public transit agency that implemented a telematics tracking system to manage its bus fleet. With the introduction of real-time tracking, the agency improved passenger information systems, allowing riders to receive accurate arrival times and service alerts. The result was a 30% increase in ridership due to improved customer satisfaction. Key contributors to this success included:
- User-Centric Design: The telematics system was designed with the passenger experience in mind, incorporating user-friendly interfaces for easy access to information.
- Community Engagement: The agency conducted outreach initiatives to inform the public about the new system, increasing its adoption and usage.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular assessment and upgrades of the telematics system ensured that it met evolving needs and incorporated user feedback.
Construction Industry Applications
In the construction sector, a prominent building contractor utilized a telematics system to monitor the equipment used on job sites. By tracking machinery usage and maintenance schedules, the contractor reduced equipment downtime by 40%, leading to significant cost savings and increased project efficiency. Factors that led to the success of this implementation included:
- Preventive Maintenance: The system provided alerts for maintenance needs, helping to avoid costly repairs and prolonging equipment lifespan.
- Resource Allocation: Managers could track which machinery was in use and where, allowing for better planning and resource allocation across multiple sites.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Access to real-time data enabled quicker decision-making and immediate responses to potential issues.
By analyzing these case studies, it’s clear that the integration of telematics tracking systems can lead to substantial improvements across various industries. Factors such as effective training, user engagement, and real-time data analytics are crucial in ensuring successful implementation and maximizing the benefits of these technologies.
Essential FAQs
What is a telematics tracking system?
A telematics tracking system combines GPS and onboard diagnostics to monitor vehicle location, speed, and performance in real-time.
How can telematics tracking systems save costs?
They help reduce fuel consumption, improve route efficiency, and lower maintenance costs through proactive vehicle monitoring.
Are telematics tracking systems used in personal vehicles?
Yes, many personal vehicle tracking systems exist for safety and navigation, enabling users to keep tabs on their vehicles.
What industries benefit most from telematics?
Industries like logistics, transportation, and construction see significant benefits from telematics due to improved operational efficiency.
How does geofencing work in telematics?
Geofencing creates virtual boundaries that trigger alerts when a vehicle enters or exits designated areas, enhancing security and monitoring.















