Cloud computing security services are essential in today’s digital landscape, providing organizations with the tools to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud technology, understanding the intricacies of cloud security becomes paramount. With a blend of innovative solutions and established best practices, these services help to mitigate risks associated with data breaches and cyber threats.
This guide delves into the various types of cloud security services available, ranging from identity and access management to advanced encryption techniques. By examining the differences between cloud security and traditional security measures, as well as the benefits of adopting these services, we aim to equip organizations with the knowledge needed to navigate their cloud security journey effectively.
Overview of Cloud Computing Security Services
Cloud computing security services encompass a wide range of measures designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud. As organizations increasingly rely on cloud environments to store sensitive information and conduct operations, the importance of robust security protocols becomes paramount. These services are critical for mitigating risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and compliance violations, allowing businesses to focus on their core activities without worrying about security threats.Key components of cloud security include identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, regulatory compliance, and threat detection.
Each of these elements plays a vital role in ensuring that data is secure and accessible only to authorized users. Understanding these components can help organizations implement effective cloud security strategies tailored to their specific needs, enhancing their overall security posture.
Key Components of Cloud Security
Exploring the core components of cloud security is essential for organizations looking to strengthen their cloud security framework. Each component addresses different aspects of security and contributes to a comprehensive approach.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM is crucial for controlling user access to cloud resources. It involves defining user roles, permissions, and authentication methods to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and applications.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. Even if data is intercepted, encryption ensures that it remains unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption keys.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, is essential for organizations storing sensitive data in the cloud. Cloud security services often include tools and frameworks to help businesses maintain compliance and avoid legal repercussions.
- Threat Detection and Response: Implementing continuous monitoring and threat detection capabilities helps organizations identify and respond to security incidents in real-time. This proactive approach minimizes the potential impact of security breaches.
Differences Between Cloud Security and Traditional Security Measures
Understanding the distinctions between cloud security and traditional security measures is vital for organizations transitioning to cloud environments. While both aim to protect data and systems, they differ significantly in several areas.Cloud security often relies on shared responsibility models, where the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer both play roles in security. In contrast, traditional security measures typically involve a single entity responsible for securing on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud security must address the complexities of multi-tenancy, where multiple customers share the same physical resources. This necessitates advanced isolation techniques to prevent data leakage between tenants, a challenge not present in traditional single-tenant environments.Another key difference lies in scalability. Cloud security solutions are designed to scale dynamically with the organization’s needs, whereas traditional measures often require significant upfront investment and resources to expand.
Cloud security emphasizes flexibility and scalability, adapting to evolving threats and business needs.
Types of Cloud Security Services
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate, but with this transformation comes the necessity for robust security measures. As organizations increasingly leverage the power of the cloud, they need to understand the various security services available to protect their data and infrastructure. This segment explores the different types of cloud security services, providing insights into each category and highlighting the benefits they bring to organizations.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a critical component of cloud security services, aimed at managing user identities and controlling access to resources. IAM solutions help organizations ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with regulations.Key benefits of IAM include:
- Enhanced Security: By implementing strong authentication methods and role-based access controls, IAM solutions significantly reduce the chances of unauthorized access.
- Improved Compliance: IAM helps organizations adhere to regulatory requirements by providing detailed audit trails and reporting capabilities.
- Streamlined User Management: Centralized user management simplifies the process of onboarding and offboarding employees, ensuring that access rights are appropriately assigned and revoked.
Leading providers such as AWS offer IAM services that allow organizations to control access to their cloud resources effectively. Microsoft Azure also has robust IAM capabilities that enable fine-grained access control and authentication.
Encryption Services
Encryption is vital for protecting data at rest and in transit. By encrypting sensitive data, organizations can ensure that even if a data breach occurs, the information remains unreadable to unauthorized users. The benefits of encryption services include:
- Data Protection: Encryption safeguards sensitive information, making it difficult for malicious actors to exploit stolen data.
- Trust and Reputation: Employing encryption fosters trust among customers and partners, as they can be assured that their data is secure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regulations mandate encryption of sensitive data, and compliance can be achieved effectively through these services.
Providers like Google Cloud Platform offer encryption both at rest and in transit, ensuring that data is protected throughout its lifecycle. Similarly, AWS provides comprehensive encryption capabilities for its various services.
Threat Detection and Response
Threat detection and response services are designed to monitor cloud environments continuously and identify potential security threats in real-time. These solutions help organizations respond swiftly to incidents, minimizing the impact on operations.Benefits of threat detection and response services include:
- Proactive Threat Management: Continuous monitoring allows for early detection of threats, enabling timely intervention before they escalate.
- Automated Response: Many services include automated response capabilities, allowing for rapid containment of threats without manual intervention.
- Enhanced Visibility: Threat detection solutions provide comprehensive insights into security events, helping organizations understand their security posture better.
Leading cloud service providers, such as IBM Cloud, offer threat detection tools that leverage machine learning to identify anomalies and potential threats. Similarly, Azure Sentinel from Microsoft provides intelligent security analytics for rapid threat detection.
“Investing in cloud security services is not just about compliance; it’s about building trust and protecting your organization’s reputation.”
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Security

Implementing robust cloud security practices is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards. As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, they must adopt a proactive approach to safeguard their digital assets from emerging threats. By following best practices tailored for cloud environments, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture.One of the fundamental aspects of cloud security is to ensure that security measures are integrated into the cloud architecture from the outset.
This includes using strong encryption methods for data both in transit and at rest, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user access, and regularly updating security protocols to reflect the latest threats. Organizations should also conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and address them proactively.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks
Regular security audits and compliance checks are crucial components of an effective cloud security strategy. These practices help ensure that security measures are functioning as intended and that the organization is in alignment with industry regulations. Conducting periodic audits can uncover weaknesses in the cloud infrastructure, enabling organizations to rectify these issues before they can be exploited. Compliance checks serve not only to adhere to legal requirements but also to foster a culture of accountability and security awareness within the organization.
Essential aspects of security audits and compliance include:
- Reviewing access controls to ensure only authorized users have access to sensitive data.
- Assessing the effectiveness of encryption protocols and data protection measures.
- Verifying that incident response plans are tested and updated regularly.
- Ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, which mandate specific security requirements.
This ongoing commitment to security audits and compliance can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and enhance trust among stakeholders.
Essential Tools and Software for Enhancing Cloud Security
To bolster cloud security, organizations should leverage a variety of tools and software designed to protect against cyber threats. These solutions provide essential functionalities such as threat detection, data encryption, and access management.A proactive security posture can be achieved through the use of the following tools:
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): These act as intermediaries between cloud service users and providers, ensuring that security policies are enforced.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions: IAM tools help manage user identities and permissions, enforcing the principle of least privilege.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems: SIEM tools aggregate and analyze security data from various sources, helping to identify and respond to threats in real time.
- Encryption Software: Utilizing encryption ensures that data is secure both in transit and at rest, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools: These tools help identify and remediate potential vulnerabilities within cloud infrastructure before they can be exploited.
By integrating these tools into their security strategies, organizations can enhance their ability to detect, respond to, and mitigate risks associated with cloud computing.
Risks and Challenges in Cloud Security
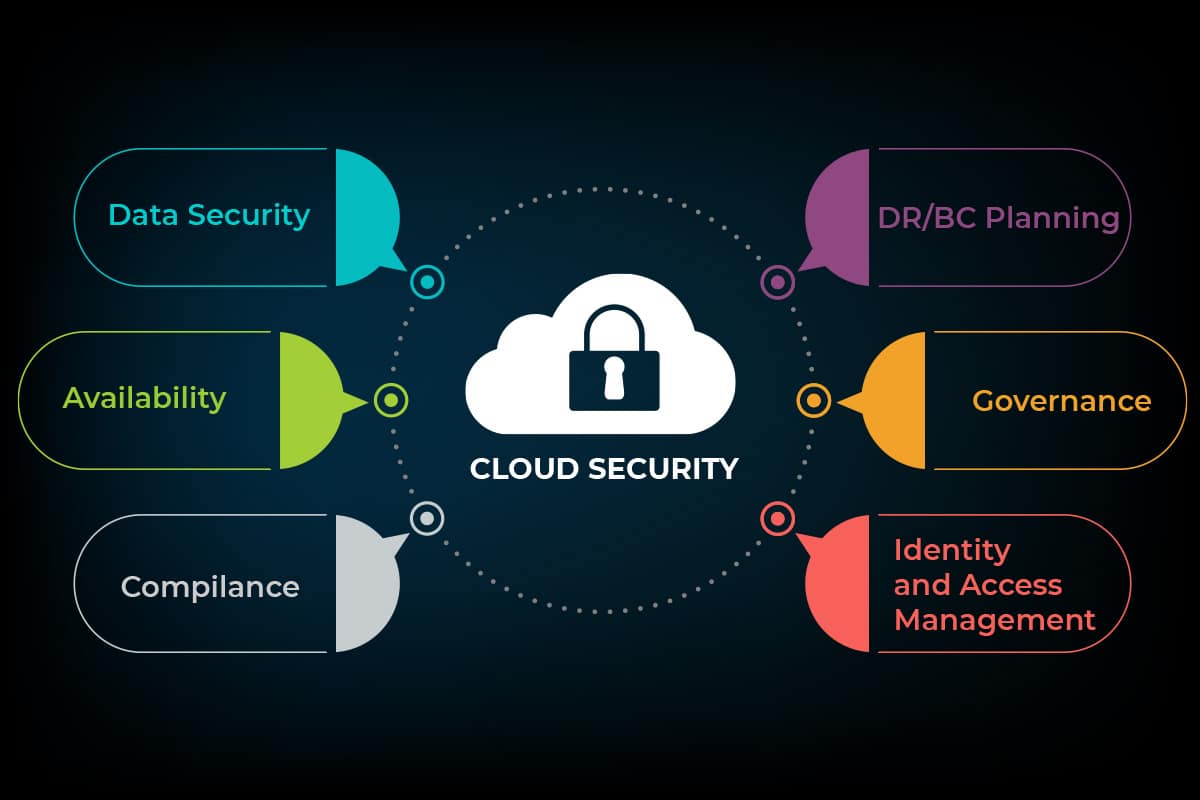
As organizations increasingly migrate to cloud computing, they face a variety of risks and challenges that can impact the security of their data and systems. Understanding these risks is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. This section delves into the major risks, common threats, and the challenges organizations encounter while implementing cloud security services.
Major Risks Associated with Cloud Computing
Several significant risks are inherent to cloud computing that organizations must consider. These risks can lead to data breaches, loss of control over sensitive information, and potential regulatory violations. Here are some of the key risks:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored in the cloud can result in severe financial and reputational damage to organizations.
- Account Hijacking: Attackers can gain control of cloud accounts, leading to unauthorized activities and data manipulation.
- Data Loss: Cloud service outages or accidental deletions can result in permanent loss of critical data, impacting business continuity.
- Insider Threats: Employees with legitimate access can intentionally or unintentionally compromise cloud security by mishandling sensitive information.
- Compliance Violations: Failure to adhere to regulatory standards can lead to legal repercussions and financial penalties.
Common Threats and Vulnerabilities in Cloud Security
The cloud environment presents multiple vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. Understanding these threats is vital for organizations to implement effective security measures. Some common threats include:
- Insecure APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that are not properly secured can be exploited, allowing attackers to manipulate cloud resources.
- Misconfiguration: Improperly configured cloud services can expose data to the public or unauthorized users, increasing the risk of breaches.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Attackers can launch DoS attacks to disrupt the availability of cloud services, hindering business operations.
- Malware Attacks: Cloud environments can serve as a medium for distributing malware, affecting both the cloud and on-premises systems.
- Data Insecurity: Data stored in the cloud may be vulnerable to interception during transfer if not properly encrypted, leading to unauthorized access.
Challenges Organizations Face When Adopting Cloud Security Services
Implementing cloud security services is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate various obstacles to ensure a secure cloud environment. Key challenges include:
- Limited Visibility: Difficulty in monitoring and managing data across multiple cloud environments can lead to security blind spots.
- Complexity of Compliance: Navigating diverse regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance in a cloud environment can be daunting.
- Resource Constraints: Smaller organizations may lack the necessary resources or expertise to implement robust cloud security measures effectively.
- Vendor Lock-In: Dependence on a specific cloud provider can make it difficult to switch vendors or integrate with other systems securely.
- Culture and Awareness: A lack of security awareness among employees can result in poor security practices, increasing vulnerability to attacks.
Effective cloud security requires ongoing vigilance, continuous monitoring, and a comprehensive understanding of the unique risks and challenges associated with cloud computing.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations

In the realm of cloud computing, adherence to compliance and regulatory standards is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring data protection. Organizations must familiarize themselves with various regulations that govern the handling of sensitive information. Understanding these frameworks not only helps in avoiding legal pitfalls but also builds a robust security posture.Organizations dealing with sensitive data must comply with several key regulations, including GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Each of these standards has specific requirements that dictate how data must be managed and protected, depending on the type of data and the industry involved.
Relevant Compliance Standards
The following compliance standards are particularly significant for organizations utilizing cloud services:
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation sets stringent guidelines for the collection and processing of personal data within the European Union. Organizations are required to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act mandates that covered entities and business associates safeguard protected health information (PHI). This includes ensuring that cloud service providers comply with HIPAA requirements through Business Associate Agreements (BAAs).
- PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard provides a framework for securing credit card transactions. Organizations handling payment card information must comply with these standards to prevent data breaches and protect cardholder data.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
To effectively meet compliance requirements, organizations should implement the following strategies:
- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure and ensure compliance with relevant standards.
- Develop and maintain a comprehensive data protection policy that Artikels how data is collected, stored, and processed within the cloud environment.
- Provide employee training on compliance standards and security practices to foster a culture of data protection across the organization.
- Utilize encryption and access controls to safeguard sensitive information both in transit and at rest.
The Role of Third-Party Audits
Engaging third-party auditors plays a vital role in the compliance landscape for cloud security. These independent assessments help verify that organizations adhere to necessary standards and can provide several benefits:
- Third-party audits offer an unbiased evaluation of an organization’s compliance with regulations, ensuring objectivity in the assessment process.
- They help identify gaps in security practices and provide actionable insights for improvement, enhancing overall data protection efforts.
- Successful audit results can enhance an organization’s reputation by demonstrating a commitment to compliance and data security, fostering trust with clients and stakeholders.
“Regular audits and compliance checks are not just about meeting regulations; they are an integral part of building a secure cloud environment.”
Adhering to compliance standards in cloud security is not a one-time effort but a continuous process that requires regular updates and monitoring. By following these practices, organizations can ensure they remain compliant while effectively protecting sensitive data from potential threats.
Future Trends in Cloud Security
As the landscape of technology continues to evolve, so too does the realm of cloud security. Organizations are increasingly relying on cloud services, which necessitates a forward-thinking approach to security practices. In the coming years, we can expect significant advancements in cloud security services, driven by emerging technologies and changing threat landscapes. The integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into cloud security presents unique opportunities and challenges.
These technologies are set to revolutionize how organizations identify and respond to security threats while also streamlining compliance processes. The potential for AI to analyze vast amounts of data quickly allows for real-time threat detection and automated responses, fundamentally changing the speed and efficiency of security operations.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Cloud Security, Cloud computing security services
The incorporation of AI and machine learning into cloud security frameworks is predicted to enhance threat detection and response capabilities significantly. Here are several key impacts that these technologies will have:
Predictive Analysis
AI algorithms can analyze historical data to identify patterns and predict future security threats.
Automated Threat Detection
Machine learning models can continuously learn from new data, enabling them to recognize and flag anomalies without human intervention.
Incident Response
Automated systems can respond to detected threats in real-time, applying predefined protocols to mitigate risks swiftly.
User Behavior Analytics
AI can monitor user activities to detect unusual behavior that may indicate a security breach.These advancements will require organizations to adapt their security strategies, enhancing their IT infrastructure to leverage these technologies effectively.
Preparing for Future Security Challenges in the Cloud
As organizations move forward with cloud adoption and integration, they must prepare for evolving security challenges. Below are some essential strategies for readiness:
Investing in Training and Awareness
Ensuring teams are knowledgeable about emerging technologies and threats is critical for effective cloud security management.
Adopting a Zero Trust Model
This security approach emphasizes verifying every user and device attempting to access resources, reducing reliance on perimeter defenses.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Organizations should implement systems that provide ongoing visibility into cloud environments, allowing them to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
Collaboration with Cloud Providers
Building strong partnerships with cloud service providers can ensure that security measures are maintained and updated in line with best practices and regulatory requirements.The shift in focus towards proactive and adaptive security measures will be essential as cloud environments become increasingly sophisticated and integrated into organizational operations.
“The future of cloud security lies in our ability to harness the power of AI and machine learning, fostering a proactive defense strategy.”
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
In the realm of cloud computing, numerous organizations have leveraged cloud security services to not only protect their assets but also enhance operational efficiency. Analyzing these case studies offers valuable insights into effective strategies and potential pitfalls in cloud security implementation. Understanding these real-world applications can significantly aid other organizations in crafting their own robust security frameworks.
Successful Implementations of Cloud Security Services
Several organizations have demonstrated the effectiveness of cloud security services through successful implementations. For instance, a leading financial institution adopted a cloud security solution that combined advanced encryption protocols with multi-factor authentication. This strategy allowed them to securely store sensitive customer data while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. The result was a 40% reduction in data breach incidents over two years.Another notable example is a global e-commerce giant that integrated a cloud-native security platform into its operations.
This platform utilized machine learning algorithms to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. The proactive nature of this approach led to a significant drop in successful phishing attacks, ultimately safeguarding customer transactions and preserving brand trust.
Lessons Learned from Cloud Security Breaches
Despite the advancements in cloud security, some organizations have faced severe breaches that have served as cautionary tales for the industry. For instance, a healthcare provider experienced a data breach that exposed millions of patient records due to misconfigured cloud storage settings. The incident highlighted the critical importance of proper configuration and ongoing security assessments, leading many companies to revisit their cloud security policies.Additionally, a high-profile breach at a social media company revealed vulnerabilities in third-party integrations.
The incident underscored the need for rigorous vetting of third-party applications and continuous monitoring to protect sensitive data from external threats.
Strategies Employed by Leading Organizations
Leading organizations have adopted various strategies to enhance their cloud security posture. The following points Artikel some of these effective practices:
- Zero Trust Architecture: Organizations are increasingly implementing a Zero Trust model, which assumes that threats could be internal or external. This approach involves strict identity verification processes for every user, device, and application accessing the network.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting routine audits and vulnerability assessments helps organizations identify and rectify potential security gaps before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Automated Security Responses: Deploying automation tools allows organizations to respond to security events swiftly, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers.
- Employee Training Programs: Comprehensive training programs for employees on security best practices are crucial, as human error often plays a significant role in data breaches.
By integrating these strategies, organizations not only fortify their defenses but also create a culture of security awareness that permeates their entire operation.
“A proactive approach to cloud security is not a luxury; it is a necessity in today’s digital landscape.”
Security Expert
FAQs: Cloud Computing Security Services
What are cloud computing security services?
Cloud computing security services are measures and tools designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud from threats and vulnerabilities.
How do cloud security services differ from traditional security measures?
Cloud security services are specifically tailored for cloud environments, addressing unique challenges like multi-tenancy and remote access, while traditional measures typically focus on on-premises infrastructure.
What are some common types of cloud security services?
Common types include identity and access management, encryption, threat detection, and security information and event management.
What role do compliance standards play in cloud security?
Compliance standards help organizations ensure that their cloud security practices meet legal and regulatory requirements, thereby protecting sensitive information and maintaining customer trust.
How can organizations prepare for future cloud security challenges?
Organizations can prepare by staying updated on emerging technologies, regularly auditing their security practices, and adopting a proactive approach to threat management.