Delving into hvac computer software, this innovative tool is transforming how we approach heating and cooling systems. As technology continues to evolve, HVAC software has become a cornerstone in the efficient design, management, and maintenance of climate control systems. From load calculations to energy modeling, the capabilities of such software not only enhance productivity but also ensure a higher degree of accuracy in installations and operations.
With various categories available, including design and management tools, HVAC software caters to both commercial and residential needs. The shift towards cloud-based solutions is changing the landscape, allowing for easier access and integration with other systems, making it more essential than ever for modern HVAC professionals to embrace these advancements.
Introduction to HVAC Computer Software
The integration of HVAC computer software into modern heating and cooling systems represents a significant advancement in building technology. This software enhances the efficiency and functionality of HVAC systems, making them more user-friendly and energy-efficient. As the demand for smarter, more responsive climate control systems continues to grow, HVAC software has become a pivotal tool for engineers, technicians, and building managers alike.
The evolution of HVAC technology has been remarkable, transitioning from purely mechanical systems to sophisticated digital solutions. Early HVAC systems relied heavily on manual controls and basic mechanical components, but the advent of computer technology has transformed these systems. Today, the development of HVAC software enables complex calculations, real-time monitoring, and automated controls that optimize performance. This evolution has resulted in increased energy savings, better indoor air quality, and reduced operational costs for both commercial and residential applications.
Key Features of HVAC Software
A wide array of features is typically incorporated into modern HVAC software, all aimed at enhancing system performance and user experience. Understanding these features is crucial for selecting the right software for specific needs. Below are some of the most significant features commonly found in HVAC software:
- Energy Modeling: HVAC software provides tools for simulating energy consumption, allowing users to forecast performance under various conditions, enabling efficient design and operation.
- Load Calculation: Accurate heat load calculations ensure optimal sizing of HVAC systems, preventing over-sizing or under-sizing, which can lead to inefficiencies.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Many systems now offer real-time data analysis, giving users instant feedback on system performance and alerts for any anomalies or maintenance needs.
- System Design Tools: Users can design ductwork and piping systems with integrated calculation capabilities, which streamline the process and ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Maintenance Management: HVAC software often includes scheduling tools for regular maintenance, helping prolong the lifespan of the equipment and maintain operational efficiency.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive interfaces allow users to easily navigate the software, making complex tasks more manageable and accessible, even for those with limited technical background.
- Integration Capabilities: Modern HVAC software can integrate with various building management systems (BMS), providing a centralized platform for controlling multiple systems from one interface.
“The right HVAC software can lead to energy savings of up to 30%, demonstrating its critical role in modern HVAC management.”
Types of HVAC Computer Software
HVAC computer software comes in various forms, each designed to cater to specific aspects of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. The right software can streamline processes, enhance accuracy, and improve overall efficiency in HVAC operations, whether for commercial or residential applications. Understanding the different types of HVAC software can aid professionals in selecting the best tools for their needs.Among the various software categories are design tools, calculation software, and management systems.
Each of these plays a crucial role in the HVAC industry by providing tailored solutions for specific tasks.
Design Tools
Design tools are essential for creating efficient and effective HVAC systems. These applications assist engineers and designers in modeling systems, ensuring that they meet required specifications and performance standards.
- AutoCAD MEP: A widely used software that integrates with AutoCAD to facilitate mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) design.
- Revit: A Building Information Modeling (BIM) tool that allows for detailed 3D modeling of HVAC systems, improving collaboration and reducing errors.
- HVAC Solution: This software provides design capabilities specifically for HVAC systems, including load calculations and duct design.
Calculation Software
Accurate calculations are vital for HVAC system efficiency. Calculation software helps professionals perform load calculations and energy analysis, ensuring that systems are appropriately sized.
- Cool Calc: A cloud-based tool that simplifies load calculations, making it accessible and user-friendly.
- Trane Trace 700: A comprehensive software for energy modeling and analysis, useful for both commercial and residential projects.
- HAP (Hourly Analysis Program): This program calculates heating and cooling loads, enabling engineers to design systems that meet specific energy needs.
Management Tools
Management software focuses on the operational aspects of HVAC systems, including maintenance scheduling, inventory management, and service dispatch.
- ServiceTitan: A robust platform that streamlines scheduling, billing, and customer management for HVAC service providers.
- FieldEdge: This software enhances field service management, offering tools for real-time communication and customer relationship management.
- eMaint: A maintenance management software that helps HVAC businesses schedule preventive maintenance and track equipment performance.
Commercial vs. Residential HVAC Software Solutions
Commercial and residential HVAC software solutions differ significantly in their features and functionalities. Commercial HVAC software often includes advanced features for large-scale systems, such as integration with building management systems and detailed reporting capabilities. Examples include Trane Trace and EnergyPlus, which address complex energy modeling needs for large buildings.On the other hand, residential HVAC software focuses on user-friendly interfaces and straightforward calculations.
Tools like Cool Calc and HVAC Solution are tailored to smaller systems, ensuring that contractors can easily perform load calculations and design efficient systems.
Cloud-based vs. On-premise HVAC Software Systems, Hvac computer software
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise HVAC software can impact flexibility, accessibility, and cost.Cloud-based systems provide the advantage of remote access, allowing users to work from various locations and collaborate in real-time. These solutions often require subscription fees and have lower upfront costs. On-premise systems are installed locally and can offer enhanced security and control, often preferred by larger organizations with specific data management requirements.
However, they come with higher initial costs and maintenance responsibilities.
The decision between cloud-based and on-premise software should consider factors such as budget, required features, and the organization’s operational model.
Benefits of Using HVAC Computer Software
The adoption of HVAC computer software presents a multitude of advantages that significantly enhance the efficiency, productivity, and cost-effectiveness of HVAC operations. By integrating sophisticated software solutions, businesses can streamline their processes, resulting in improved performance and reliability across various aspects of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity in HVAC Operations
Utilizing HVAC software allows for the automation of numerous tasks that were traditionally manual, leading to remarkable gains in efficiency. This software facilitates real-time monitoring and management of HVAC systems, ensuring optimal performance. Key benefits include:
- Streamlined project management helps keep resources allocated efficiently.
- Enhanced scheduling capabilities optimize service and maintenance calls, reducing downtime.
- Automated reporting tools provide insights into system performance, which can lead to proactive measures and timely interventions.
- Collaboration features enable better communication between teams, improving workflow and project outcomes.
Enhanced Accuracy in System Design and Installation
Accuracy is paramount in HVAC design and installation, as it directly impacts system performance and energy efficiency. HVAC software incorporates advanced modeling tools that help engineers and technicians create precise designs tailored to specific building needs. The advantages of these tools include:
- Accurate load calculations ensure the correct sizing of equipment, minimizing the risk of oversizing or undersizing systems.
- 3D modeling capabilities allow for visualizing installations, reducing errors during the installation process.
- Built-in regulations and standards help ensure compliance, reducing the chances of costly rework.
- Simulation features predict system performance, allowing for adjustments before installation.
Cost Savings Associated with Using HVAC Software for Maintenance and Support
Investing in HVAC software can lead to significant cost savings over time, particularly in maintenance and support. By leveraging software for predictive maintenance, companies can avoid expensive repairs and unscheduled downtimes. Important aspects include:
- Predictive analytics help identify potential system failures before they occur, enabling timely interventions.
- Centralized documentation supports easy access to historical data, streamlining maintenance processes.
- Energy management tools facilitate monitoring and optimizing energy usage, leading to lower utility bills.
- Cost-effective maintenance scheduling extends the life of equipment, resulting in reduced capital expenditure.
Features and Functionalities

HVAC software is designed to streamline the complex processes involved in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning design and management. Understanding the essential features and functionalities of this software can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy in HVAC projects. Below are crucial aspects that highlight the capabilities of modern HVAC software.
Essential Features of HVAC Software
A robust HVAC software platform offers a variety of features that facilitate effective design, analysis, and management of HVAC systems. These features include:
- Load Calculation: This function allows engineers to determine the heating and cooling requirements of a space, ensuring optimal equipment selection and energy efficiency.
- Energy Modeling: Energy modeling features simulate the energy consumption and efficiency of HVAC systems, predicting performance under various conditions and setups.
- Simulation Tools: Advanced simulation tools enable users to visualize system performance over time, considering variations in external factors like weather and building occupancy.
- Equipment Selection: Many HVAC software applications include tools to assist in selecting appropriate components based on project specifications and calculated loads.
- Integration Capabilities: Modern HVAC software can often integrate with other construction and building management systems, providing a seamless workflow from design to implementation.
Reporting Capabilities and Data Visualization
Reporting and data visualization are key functionalities of HVAC software that help in analyzing performance and making informed decisions. Effective reporting tools allow users to generate insightful documents that summarize critical data.
- Performance Reports: Users can generate detailed reports that assess the efficiency and performance of HVAC systems over time.
- Energy Usage Graphs: Visual representations of energy consumption help identify patterns and inefficiencies, allowing for targeted improvements.
- Cost Analysis Tools: These tools provide insights on operational costs, helping to justify design choices and identify potential savings.
“Effective reporting and data visualization allow HVAC professionals to present data in a clear and actionable manner, influencing project decisions and outcomes.”
User Interface Design and User Experience
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of HVAC software play a significant role in its effectiveness. A well-designed UI enhances usability, allowing users to navigate the software effortlessly.Several key considerations in UI and UX design include:
- Intuitive Navigation: Menus and features should be organized logically, enabling users to find the tools they need without confusion.
- Customizable Dashboards: Personalization options allow users to arrange widgets and tools according to their workflow preferences, enhancing productivity.
- Accessibility Features: Design should accommodate users of varying skill levels and abilities, ensuring that everyone can effectively utilize the software.
- Responsive Design: Compatibility with various devices ensures that users can access the software on desktops, tablets, or smartphones without loss of functionality.
In conclusion, the features and functionalities of HVAC software are vital for performing accurate calculations, enhancing project efficiency, and ensuring user satisfaction through thoughtful design. The integration of these capabilities ultimately leads to better HVAC solutions and improved energy management.
Choosing the Right HVAC Software: Hvac Computer Software
Selecting the appropriate HVAC software is crucial for optimizing efficiency, enhancing productivity, and ensuring customer satisfaction in HVAC operations. With a plethora of options available, it’s essential to navigate the selection process carefully to meet specific business needs and objectives. When deciding on HVAC software, various factors must be taken into account to ensure it aligns with operational requirements and future growth.
Evaluating the features and functionalities that best match the intended applications is vital.
Factors to Consider When Selecting HVAC Software
Identifying the right HVAC software requires a clear understanding of your business’s operational needs, as well as an assessment of various software capabilities. Below are key factors to consider:
- Scalability: The software should be able to grow with your business. Consider if it can accommodate an increasing number of users or projects.
- Integration: Ensure the software can integrate with existing systems such as accounting or CRM software for seamless data flow.
- User-Friendliness: A user-friendly interface reduces the learning curve for employees and minimizes training time.
- Mobile Access: Given the mobile nature of HVAC work, having software accessible on mobile devices can improve efficiency in the field.
- Reporting Capabilities: Robust reporting tools help in tracking performance, analyzing trends, and making data-driven decisions.
Checklist for Evaluating Software Features Against Business Needs
Creating a checklist can streamline the evaluation process, ensuring that all critical features are assessed before making a final decision. Here’s a comprehensive checklist that can be useful:
- Does the software support the specific HVAC tasks required by your business?
- Are there automation features that can save time on repetitive tasks?
- Is there a built-in customer relationship management (CRM) system?
- Does the software provide accurate calculations for load estimation and system design?
- What is the level of customer support and training offered by the vendor?
- Are there reviews or testimonials from other HVAC professionals regarding this software?
Importance of Customer Support and Training in Software Selection
When selecting HVAC software, the importance of customer support and training cannot be overstated. Effective customer support ensures that any technical issues can be resolved quickly, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions. Training is essential, as it equips employees with the necessary skills to use the software effectively. A software solution with comprehensive training resources—such as tutorials, manuals, and webinars—can facilitate smoother onboarding and enhance overall productivity.
“Investing in robust training and customer support can significantly enhance software adoption and in turn, optimize business processes.”
In conclusion, making an informed choice about HVAC software involves careful consideration of various factors, thorough evaluation through a tailored checklist, and acknowledgment of the importance of customer support and training in maximizing the software’s potential.
Integration with Other Systems
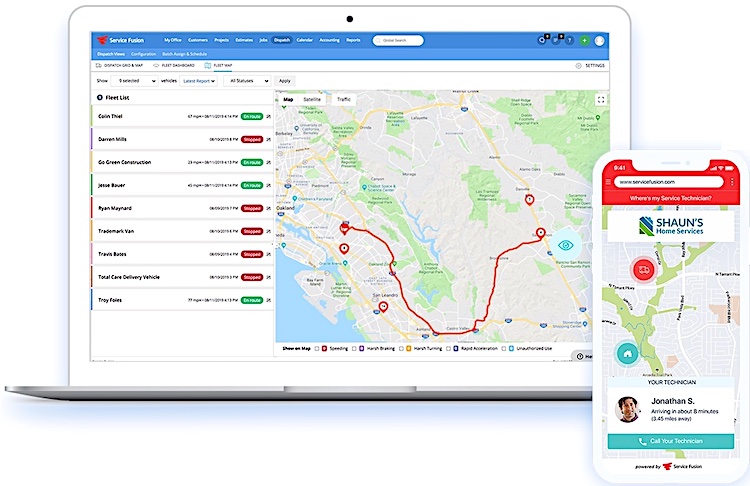
The integration of HVAC software with other systems is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and ensuring seamless communication among different building components. Modern HVAC solutions are designed to work in harmony with various systems, enhancing overall functionality and providing valuable data insights. By connecting HVAC software with other systems, businesses can optimize energy usage, streamline maintenance processes, and improve occupant comfort.
Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS)
HVAC software plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of Building Management Systems (BMS). A BMS consolidates data from various building systems, including HVAC, lighting, security, and energy management, to provide centralized control and monitoring. Integration allows HVAC systems to receive commands and share data with the BMS, thereby enabling coordinated operation.This integration results in many benefits, including:
- Real-time monitoring of HVAC performance metrics such as temperature, humidity, and energy consumption.
- Synchronized control of HVAC systems with other building systems to maintain optimal conditions.
- Automated reporting and alerting mechanisms that notify maintenance teams of potential issues.
Interoperability with Trade-Specific Software
The interoperability of HVAC software with other trade-specific applications, such as electrical and plumbing software, is vital for efficient project execution. When these systems work together, they help create a comprehensive framework where various trades can collaborate effectively.Benefits of this interoperability include:
- Accurate load calculations and system design through shared data between HVAC and electrical systems.
- Streamlined project workflows, allowing for coordinated scheduling and resource allocation.
- Improved compliance with building codes and regulations by ensuring all trades adhere to the same standards.
Data Exchange with IoT Devices
The integration of HVAC software with Internet of Things (IoT) devices is revolutionizing the way HVAC systems operate. IoT devices, such as smart thermostats, sensors, and energy meters, collect data that can be transmitted to HVAC software for analysis and decision-making.Key methods of data exchange include:
- Using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for real-time data transfer between HVAC systems and IoT devices, enabling dynamic adjustments based on environmental conditions.
- Employing protocols like MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) or BACnet to facilitate communication and interoperability among devices.
- Utilizing cloud platforms to store and analyze data collected from IoT devices, allowing for advanced analytics and predictive maintenance.
Future Trends in HVAC Software Development
The HVAC industry is on the brink of major technological advancements that are set to redefine software development. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly paramount, HVAC software is also evolving to integrate cutting-edge technologies. This section delves into the trends shaping the future of HVAC software, exploring the role of artificial intelligence, energy standards, and shifting user demands.
Emerging Technologies in HVAC Software
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming HVAC software by enabling predictive analytics and automated decision-making. These technologies facilitate better management of HVAC systems, optimizing performance and energy use. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict equipment failures before they happen, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. The integration of smart sensors further enhances this capability, providing real-time data that improves system efficiency.The shift towards smart buildings is also increasing the reliance on IoT (Internet of Things) technologies.
With connected devices, HVAC systems can communicate with other building management systems, leading to more streamlined operations. The rise of cloud computing is allowing for greater data storage and processing capabilities, making it easier for HVAC professionals to access and analyze data from anywhere.
Impact of Energy Efficiency Standards
Energy efficiency standards are becoming more stringent around the globe, driving innovation in HVAC software development. As regulations evolve, HVAC software must adapt to ensure compliance while optimizing energy consumption. Manufacturers are expected to develop software that not only meets these standards but also provides detailed analytics on energy usage.This shift can encourage the development of features such as real-time energy monitoring and reporting tools, which help users track their energy consumption patterns and identify areas for improvement.
Companies that effectively leverage these standards can enhance their competitive edge by promoting energy-efficient solutions, aligning with regulatory requirements while appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
User Demands Shaping New Features
As the HVAC market grows, so do user expectations. End-users are looking for more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces within HVAC software. Customizability is becoming a key factor; users want the ability to tailor software solutions to fit their specific needs. Software developers are responding by incorporating features that enhance the user experience, such as:
- Mobile access: Users increasingly expect to manage HVAC systems remotely through mobile applications, allowing for flexibility and convenience.
- Integration capabilities: The demand for seamless integration with other building management systems is driving software developers to create solutions that work well with existing technologies.
- Data visualization: Users benefit from clear, visual representations of complex data, making it easier to interpret and act upon information.
Incorporating feedback from users in the early stages of software development is vital. Companies that prioritize user experience are likely to see increased satisfaction and loyalty from their customers.
“The future of HVAC software lies in the seamless integration of emerging technologies, user expectations, and regulatory compliance.”
General Inquiries
What are the main benefits of using HVAC software?
The main benefits include improved efficiency, enhanced accuracy in design and installation, and cost savings on maintenance and support.
How does HVAC software integrate with other systems?
HVAC software can integrate with building management systems and is often interoperable with other trade-specific software, allowing for seamless data exchange.
What should I consider when choosing HVAC software?
Consider factors such as specific application needs, feature evaluation against business requirements, and the availability of customer support and training.
What are some emerging trends in HVAC software?
Emerging trends include the use of AI and machine learning, as well as evolving energy efficiency standards that drive innovation in software features.
Is cloud-based HVAC software better than on-premise solutions?
Cloud-based solutions offer advantages like remote access and easier updates, while on-premise systems may provide more control over data and security.