Payroll computer software is revolutionizing the way businesses handle their payroll processes, making tasks quicker and more efficient. As organizations grow and evolve, the need for streamlined payroll management becomes increasingly vital. This software not only saves time but also minimizes errors associated with manual calculations, ensuring accuracy and compliance with tax regulations.
With various types of payroll software available, from cloud-based solutions to on-premise applications, businesses can choose options that best fit their needs. This introduction to payroll computer software will explore its features, benefits, and best practices for implementation and integration, providing a comprehensive understanding for any organization looking to enhance their payroll management.
Overview of Payroll Computer Software
Payroll computer software serves as a crucial tool for businesses, streamlining the process of managing employee compensation and ensuring compliance with legal requirements. By automating various payroll functions, these systems not only save time but also enhance accuracy, ultimately contributing to improved employee satisfaction and operational efficiency.The fundamental purpose of payroll software lies in its ability to compute wages, track hours worked, and manage deductions efficiently.
Traditional payroll processing can be time-consuming and prone to errors, often resulting in employee dissatisfaction and potential legal repercussions. In contrast, payroll software offers numerous benefits, including reduced processing time, minimized errors, and simplified tax compliance.
Key Features of Payroll Software
Payroll software distinguishes itself from manual payroll processing through several key features that enhance productivity and accuracy. Understanding these features can help businesses appreciate why transitioning to automated solutions is beneficial.
Automated Calculations
Payroll software automatically calculates employee wages, taxes, and deductions, eliminating the need for manual calculations that can lead to mistakes.
Real-Time Data Management
Employees can log their hours and access payroll information in real-time, ensuring they are always informed about their compensation status.
Easy Tax Filing
Many payroll systems integrate with tax agencies, allowing for easier filing of tax forms and ensuring that the business remains compliant with current tax laws.
Employee Self-Service
Most payroll software includes self-service portals where employees can view their pay stubs, request time off, and update personal information, reducing administrative workloads.
Reporting Capabilities
The software provides detailed reports on payroll expenses, which help in budget planning and financial decision-making.
Evolution of Payroll Software
The evolution of payroll software reflects the ongoing advancements in technology and business practices. Early payroll systems relied heavily on manual processes involving paper records and calculators, which were labor-intensive and often inaccurate. As businesses grew, the demand for more efficient methods led to the development of computerized payroll systems.Initially, payroll software was focused on simplifying calculations and record-keeping. However, advancements in technology have led to features that now include cloud-based solutions, mobile access, and robust data analytics.
These modern solutions not only enhance functionality but also provide businesses with valuable insights into their labor costs and workforce management.
From Manual to Automated
The transition from manual methods to automated payroll systems marked a significant milestone in payroll processing. The introduction of personal computers in the 1980s allowed companies to shift payroll functions from ledgers to digital formats.
Rise of Cloud-Based Solutions
In the 2000s, cloud technology revolutionized payroll software, enabling remote access and reducing the need for on-premises hardware. This shift has facilitated scalability and easier updates.
Integration with HR Systems
Today’s payroll solutions often integrate seamlessly with HR management systems, providing a holistic view of employee data and enhancing overall business operations.Overall, payroll computer software has evolved from basic calculation tools into sophisticated systems that provide comprehensive management of employee compensation and related processes, significantly enhancing efficiency and accuracy for businesses of all sizes.
Types of Payroll Computer Software
Payroll software has evolved significantly to cater to different business needs, and understanding the types available can help businesses make informed choices. With various options like cloud-based and on-premise solutions, each type presents unique advantages depending on the organization’s size, structure, and operational requirements.One of the primary distinctions in payroll software is between cloud-based solutions and on-premise installations. Cloud-based payroll software is hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet, allowing businesses to manage payroll from anywhere with internet access.
On the other hand, on-premise software is installed locally on company computers, providing control over data but often requiring more maintenance and technical expertise.
Comparison of Payroll Software for Small Businesses and Larger Enterprises
When selecting payroll software, the size of the business plays a crucial role in determining which features are essential. Small businesses typically require software that is user-friendly, cost-effective, and capable of handling basic payroll functions, while larger enterprises often need more robust solutions with advanced functionalities. Small business payroll solutions often include:
- Ease of Use: Simplified interfaces that do not require extensive training.
- Affordability: Pricing structures geared toward limited budgets, often with basic functionalities.
- Basic Reporting: Essential reporting features that cover standard payroll needs without complex analysis.
Conversely, payroll solutions for larger enterprises offer:
- Advanced Features: Comprehensive options like benefits administration and compliance tracking.
- Integration Capabilities: Ability to integrate with other enterprise systems like HR and accounting software.
- Scalability: Solutions that can grow with the business and handle a larger volume of employees and transactions.
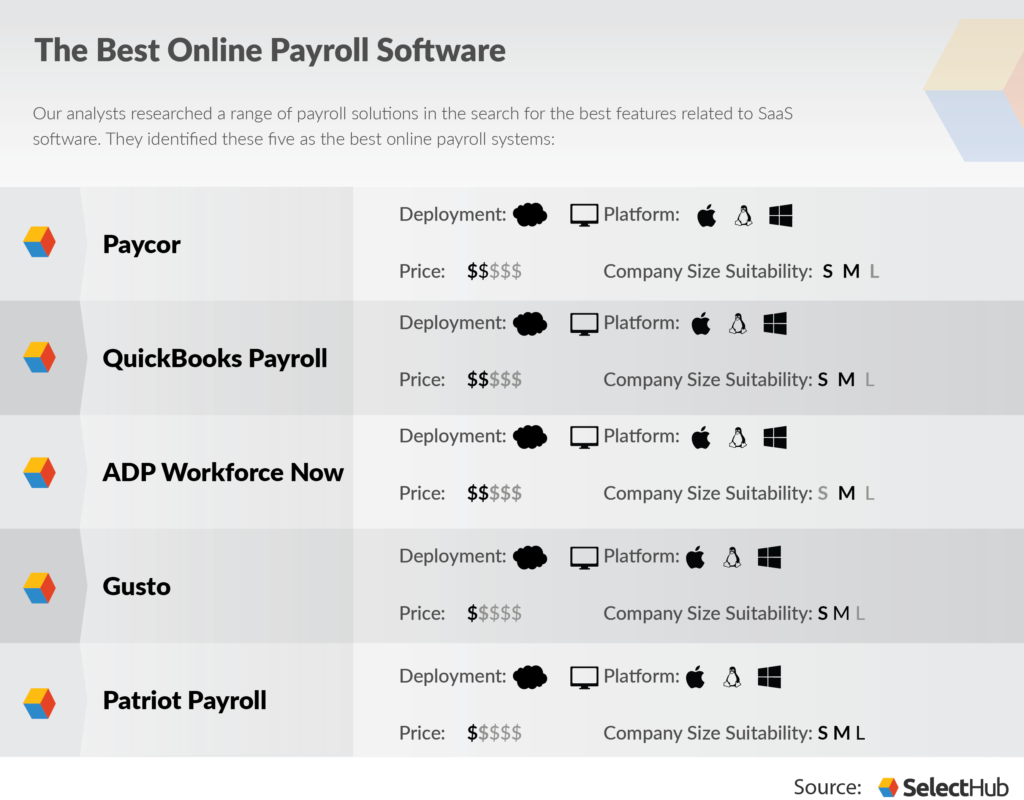
Examples of Popular Payroll Software Applications
Several payroll software applications are well-regarded for their functionalities and usability across different business sizes. Below are some notable examples:
| Software Name | Main Functionalities |
|---|---|
| QuickBooks Payroll | Offers full-service payroll, automated tax calculations, and employee self-service portals. |
| Gusto | User-friendly platform providing payroll processing, employee benefits management, and compliance assistance. |
| ADP Workforce Now | A comprehensive suite designed for larger businesses, including HR management, talent acquisition, and analytics. |
| Paychex Flex | Cloud-based payroll software that integrates HR services, employee benefits, and compliance tools. |
By evaluating these types of payroll software and their specific features tailored for both small businesses and larger enterprises, organizations can choose the solution that best aligns with their operational goals and employee management needs.
Implementation of Payroll Software
Implementing payroll software is a significant step for any organization aiming to streamline its payroll processes. Effective payroll management not only ensures employees are paid accurately and on time but also maintains compliance with tax laws and regulations. The implementation process, however, requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition from manual or outdated systems.The successful implementation of payroll software involves several well-defined steps that organizations must follow to maximize efficiency.
These steps help in determining the right software tailored to the needs of the organization, ensuring that all resources and data are available for a seamless setup.
Steps Required to Implement Payroll Software
The implementation process can be broken down into key stages that organizations must work through. These stages ensure a structured approach, reducing the risk of errors and inefficiencies.
- Assess Needs: Evaluate the current payroll process and identify specific requirements that the software must fulfill. This includes understanding the size of the workforce, types of payments, and reporting needs.
- Research Options: Explore various payroll software options available in the market. Consider factors such as features, pricing, customer reviews, and vendor support.
- Vendor Selection: Choose a vendor based on the research. Consider conducting demos or trials to get a feel for the software and ensure it meets organizational needs.
- Gather Data: Collect all necessary employee information, including tax details, benefits, and payment histories, to ensure a smooth data transfer.
- Software Configuration: Set up the software according to organizational requirements. This may include configuring pay rates, benefits, and deductions.
- Testing: Conduct a test run of the software to catch any errors or discrepancies before going live. This is crucial for identifying potential issues.
- Training: Train HR and payroll staff on how to use the new software effectively. Ensure everyone understands the system to minimize errors during actual payroll processing.
- Go Live: Launch the software for actual payroll processing, monitoring the system closely for any issues that may arise in the initial stages.
Key Considerations During the Selection Process
When selecting payroll software, organizations must keep several key considerations in mind to ensure they choose a solution that aligns with their operational needs and goals.
Choosing the right payroll software is crucial for minimizing errors and ensuring compliance.
- Scalability: The software should accommodate workforce growth without requiring a complete overhaul.
- User-Friendliness: A straightforward interface is essential for ease of use and quick onboarding.
- Integration Capabilities: Consider how well the software can integrate with existing systems, such as HR management or accounting software.
- Compliance Features: Ensure the software automatically updates to reflect changes in tax laws and regulations.
- Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing, maintenance, and training expenses.
- Customer Support: Reliable vendor support is essential for resolving issues quickly during and after implementation.
Checklist of Necessary Data and Resources
A successful payroll software implementation requires careful preparation and the right resources. The following checklist Artikels the essential data and resources needed for a flawless transition.
Having the right data and resources at hand is key to a successful payroll implementation.
- Employee Data: Collect personal information, tax identification numbers, and wage rates.
- Payroll Policies: Document organizational payroll policies, including pay schedules, deductions, and bonuses.
- Historical Payroll Data: Gather past payroll data for accurate processing and reports.
- Banking Information: Ensure you have up-to-date banking details for direct deposits.
- Compliance Documents: Compile relevant documents related to tax regulations and employment laws.
- Software Licensing Agreements: Review and finalize agreements with the software vendor before implementation.
- IT Resources: Secure IT support for data migration and system integration during the transition.
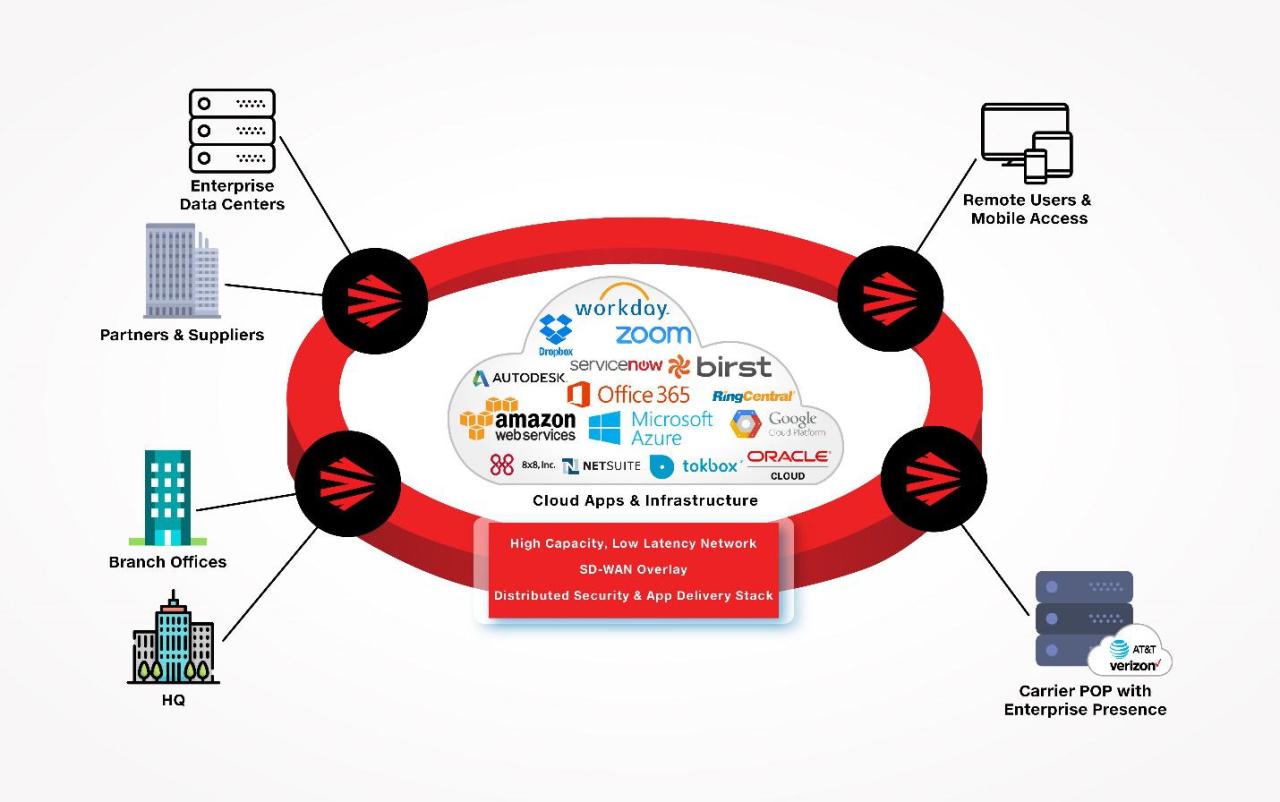
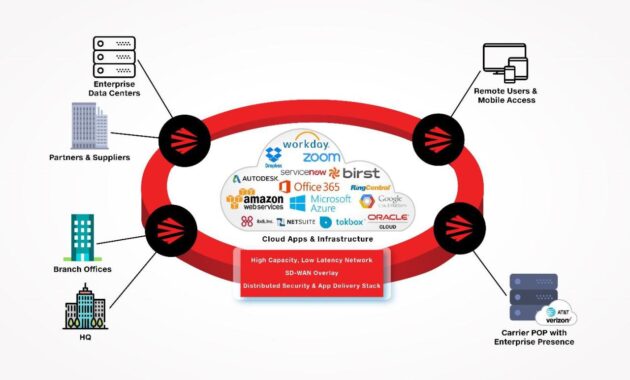
Integration with Other Systems: Payroll Computer Software

Integrating payroll software with other systems is essential for streamlining operations and enhancing overall efficiency in an organization. When payroll software communicates seamlessly with HR, accounting, and time-tracking systems, it reduces manual entry errors and saves valuable time. This integration allows organizations to manage employee information, financial records, and work hours more effectively, leading to a more coherent approach to payroll processing.
Integration with HR and Accounting Systems
Integrating payroll software with HR and accounting systems is crucial for maintaining accurate and up-to-date records. The synergy between these systems ensures that employee data, such as salaries, tax withholdings, and benefit deductions, is consistent across all platforms. This minimizes discrepancies and helps maintain compliance with tax regulations. Furthermore, payroll data can feed directly into accounting systems for streamlined financial reporting.
Some methods to ensure smooth data transfer include:
- Utilizing APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allow different software systems to communicate and share data in real time.
- Batch Data Imports: Scheduling regular imports of employee data ensures that all systems are synchronized without manual intervention.
- Cloud-based Solutions: Cloud technology facilitates easy access and integration between systems, regardless of their physical locations.
A key point to remember is that compatibility between systems is paramount. If the payroll system does not align with the HR or accounting software, it can lead to data mismanagement, increased operational costs, and compliance issues.
Time-Tracking System Integration
Integrating payroll software with time-tracking systems is a vital component in ensuring accurate payroll calculations. This integration allows for automatic updates of employee worked hours, overtime, and leave balances, ensuring that payroll is processed based on actual time worked without manual calculations.
To enhance efficiency during the integration process, consider the following:
- Real-time Data Synchronization: Implementing systems that update in real time can help eliminate discrepancies between reported hours and payroll.
- Standardized Data Formats: Ensuring that the data formats used across systems are standardized can significantly reduce integration errors.
- User Training: Providing comprehensive training for employees on how to use the integrated systems can enhance data accuracy and reduce reliance on manual processes.
An important aspect of this integration is ensuring that all systems are up to date with the latest technology, which can greatly enhance their ability to communicate effectively.
“Effective integration of payroll software with other systems leads to improved accuracy, reduced errors, and significant time savings.”
Compliance and Security Considerations
In the realm of payroll software, compliance with tax laws and labor regulations is paramount. Organizations must ensure that their payroll systems are not only efficient but also legally sound to avoid potential penalties and catastrophic consequences. The security aspect is equally crucial, given the sensitivity of employee data involved in payroll processing.Compliance requirements for payroll software encompass a variety of tax laws and labor regulations that differ by jurisdiction.
This can include federal, state, and local tax regulations, as well as labor laws governing employee rights and wages. It is vital for payroll software to accurately calculate and withhold taxes, manage contributions to retirement plans, and comply with labor standards such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
Compliance Requirements
Payroll software must adhere to several compliance requirements, including but not limited to:
- Accurate calculation of federal and state income taxes
- Social Security and Medicare tax compliance
- Adherence to unemployment insurance regulations
- Compliance with the Fair Labor Standards Act regarding minimum wage and overtime pay
- Management of employee benefits and deductions in accordance with applicable laws
Ensuring compliance is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing vigilance to stay current with ever-changing laws and regulations. Regular updates to the payroll software are necessary to incorporate these changes and maintain accuracy in payroll processing.
Data Security Best Practices
Securing sensitive employee information is a critical responsibility for any organization utilizing payroll software. Implementing robust security measures is essential to mitigating risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.Key best practices for ensuring data security include:
- Utilizing encryption to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest
- Implementing multi-factor authentication for accessing payroll systems
- Regularly updating software to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security
- Conducting regular security audits and risk assessments
- Training employees on data security awareness and best practices
A proactive approach to security can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, which can lead to severe financial and reputational damage.
Importance of Regular Updates
Regular updates to payroll software help organizations maintain compliance with changing laws and security standards. As tax regulations and labor laws evolve, failure to keep software current can result in inaccurate payroll calculations and legal issues.Organizations should prioritize the following for effective software maintenance:
- Adopting a schedule for regularly checking for software updates and patches
- Staying informed about upcoming regulatory changes and their implications for payroll
- Engaging with software support services to ensure access to the latest features and compliance tools
- Allowing for testing of updates in a controlled environment before full implementation
By ensuring that payroll software is consistently updated and supported, businesses can mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and safeguard employee data effectively.
Cost Analysis of Payroll Software
Evaluating the costs associated with payroll software is essential for businesses looking to streamline their payroll processes while maintaining budgetary constraints. The choice between subscription models and one-time purchases can significantly impact the overall financial strategy of an organization. Understanding the potential hidden costs is just as crucial, as these can erode the savings promised by adopting new technology. This section highlights the various financial aspects related to payroll software to guide informed decision-making.
Comparison of Costs in Payroll Software
When analyzing payroll software options, businesses typically encounter two primary pricing models: subscription-based services and one-time purchase solutions. Each model has its advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully considered.
- Subscription Models: These typically involve monthly or annual fees, which can range from $10 to $200 per month depending on the features and number of employees. This model allows for easier budgeting and often includes updates and customer support at no additional cost.
- One-Time Purchases: This approach requires a larger upfront investment, often between $1,000 and $10,000. While it may seem cost-effective long-term, companies should factor in the costs of updates, which may require additional purchases.
Identification of Hidden Costs
While the visible costs of payroll software are critical, hidden costs can significantly affect the total expenditure. It’s important for businesses to be aware of these additional financial commitments.
- Maintenance Fees: Ongoing support and maintenance can incur extra charges, especially for one-time purchases, which might need periodic updates.
- Training Costs: Implementing a new payroll system may require training employees, either through hiring external trainers or allocating time for internal training sessions, which can divert resources from other critical tasks.
- Integration Expenses: If the payroll software needs to be integrated with existing systems like HR or accounting software, additional integration fees may apply, along with potential downtime during the transition.
Long-Term Financial Benefits of Payroll Software
Investing in effective payroll software can yield substantial long-term financial benefits. While initial costs may seem daunting, the return on investment (ROI) can be significant.
- Time Savings: Automated payroll processes can save hours each month, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks, thus increasing overall productivity.
- Reduction in Errors: Automated calculations reduce the likelihood of mistakes that can lead to costly penalties or employee dissatisfaction.
- Improved Compliance: Many payroll solutions come with built-in compliance tools that help organizations stay updated with current laws and regulations, avoiding costly fines.
“Investing in payroll software is not just an expense; it’s a strategic move that can enhance operational efficiency and drive down long-term costs.”
User Experience and Training
User experience (UX) plays a vital role in the successful adoption of payroll software, influencing how easily employees and administrators navigate the system. A positive user experience can lead to increased productivity, reduced errors, and higher satisfaction among users. By focusing on intuitive design and accessible resources, organizations can enhance both the functionality and usability of their payroll systems.Creating a training program is essential for ensuring that staff can effectively utilize payroll software.
A well-structured program should encompass both initial training sessions and ongoing support to address evolving needs. This approach encourages familiarity with the software, ultimately leading to a more efficient payroll process.
Strategies for Enhancing User Experience, Payroll computer software
Improving user experience with payroll software requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses design, accessibility, and user feedback. Key strategies include:
- Intuitive Interface: Ensure the software has a user-friendly interface that allows users to navigate easily through functions, minimizing the learning curve.
- Personalization: Enable customization options so users can tailor their dashboards and reports according to their specific needs and preferences.
- Mobile Access: Provide a mobile-friendly platform that allows employees to access payroll information and perform tasks on the go, enhancing flexibility.
- Regular Updates: Continuously update the software based on user feedback to refine features and address common pain points.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate visual aids such as infographics or step-by-step guides that simplify complex processes within the software.
Training Program for Staff
An effective training program is crucial for empowering staff to leverage payroll software efficiently. Components of a comprehensive training program may include:
- Orientation Sessions: Provide initial training that covers the basics of the software, including navigation, data entry, and report generation.
- Hands-On Workshops: Organize practical workshops where users can engage with the software in real-time, allowing them to apply what they’ve learned.
- Resource Materials: Distribute manuals, quick reference guides, and online tutorials to serve as ongoing resources for staff.
- Regular Refresher Courses: Schedule periodic refresher courses to update employees on new features and functionalities as the software evolves.
- Peer Support System: Establish a peer mentorship program where more experienced users assist newcomers, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
Importance of User Support and Resources
User support is crucial in ensuring that employees can resolve issues and continue performing their tasks without disruption. The availability of support resources directly impacts user satisfaction and productivity. Essential support mechanisms include:
- Help Desk Services: Implement a dedicated help desk that users can contact for assistance with technical problems or software navigation.
- Online FAQs and Forums: Maintain a comprehensive online FAQ section and user forums where common issues and solutions are discussed, promoting self-service troubleshooting.
- Video Tutorials: Create video tutorials that provide step-by-step guidance on using various features of the payroll software.
- Feedback Channels: Establish channels for users to submit feedback regarding their experiences, ensuring continual improvement of the software.
- Emergency Support Options: Offer emergency support options for urgent issues that may arise during payroll processing, ensuring minimal downtime.
Future Trends in Payroll Software
The landscape of payroll software is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business requirements. As organizations strive for greater efficiency and accuracy in payroll processing, payroll software is increasingly incorporating innovative features that leverage emerging technologies. This section explores the trends shaping the future of payroll software, focusing on artificial intelligence, automation, and user preferences.
Emerging Technologies in Payroll
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are at the forefront of transforming payroll processes. These technologies enable software to handle repetitive tasks with precision, drastically reducing human error and processing time. The integration of AI allows for predictive analytics, which can help organizations forecast payroll expenses and identify potential discrepancies before they become issues. As businesses demand more efficiency, the adoption of robotic process automation (RPA) is set to streamline various payroll functions.
“AI and automation will redefine payroll processes, allowing HR departments to focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative overhead.”
The implementation of machine learning algorithms within payroll systems can enhance data processing capabilities, enabling real-time updates and providing valuable insights based on historical payroll data. This approach not only accelerates payroll processing but also aids in compliance by ensuring that all updates adhere to the latest regulations.
Anticipated Changes in Payroll Software Features
The future of payroll software will likely see a shift towards more customizable and flexible solutions, accommodating the diverse needs of businesses. Features that enhance user experience are gaining traction, such as intuitive interfaces and mobile accessibility, allowing employees to access their payroll information on-the-go. Businesses will increasingly prioritize the following features in payroll software:
- Real-time reporting and analytics capabilities for better decision-making.
- Seamless integration with other business systems, such as HR management and accounting software.
- Enhanced self-service options for employees, fostering transparency and engagement.
- Robust compliance tracking tools to simplify adherence to evolving labor laws and tax regulations.
These features reflect the need for payroll solutions that not only meet current demands but also anticipate future challenges.
Trends in User Preferences for Payroll Software Functionalities
As businesses evolve, user preferences for payroll software are shifting towards greater simplicity and efficiency. Users are increasingly looking for functionalities that enhance their experience and streamline processes. This includes the rise of mobile-friendly applications, making it easier for employees to manage their payroll details from their smartphones. Additionally, there is a growing demand for more robust self-service capabilities, allowing employees to manage their own information and access resources without needing HR intervention.
Companies are also recognizing the importance of user-friendly interfaces, which can significantly reduce the learning curve associated with new payroll systems.The emphasis on a more collaborative experience between employees and payroll systems is evident. Organizations are focusing on integrating employee feedback into the payroll software development process to ensure that the end product meets real-world needs and enhances user satisfaction.In summary, the future of payroll software is set to be shaped by technological advancements, user-centric design, and the need for adaptability in a constantly changing business environment.
Organizations that leverage these trends will be better positioned to meet their payroll needs efficiently and effectively.
User Queries
What are the primary benefits of payroll computer software?
The main benefits include increased accuracy, time savings, easy compliance with tax regulations, and improved employee satisfaction.
Can payroll software handle multiple payment schedules?
Yes, most payroll software can accommodate various payment schedules, including weekly, bi-weekly, and monthly.
How secure is payroll software regarding employee data?
Payroll software often includes encryption and secure access protocols to protect sensitive employee information.
Is it difficult to transition from manual payroll to software?
The transition can involve a learning curve, but with proper training and support, it can be relatively straightforward.
Are there any hidden costs associated with payroll software?
Yes, potential hidden costs may include training fees, maintenance, and additional charges for support or updates.